This story is the first of Climate Home News’ four-part series “The human cost of sugar”, supported by the Pulitzer Center.
“I won’t ever recover what I invested,” said 67-year-old Kalua Mehmood, a sugarcane farmer in Shahabpur, a village in western Uttar Pradesh, in northern India. Due to scarce rainfall, his sugarcane farm will deliver a poor harvest this year.
The rainfall during the monsoon season, between June and September, was erratic this year, he told Climate Home News. 10 years ago, farmers could count on steady rainfall. “But this year I have already irrigated my crop 10 times with a tube well [diesel pump] and even now the sugarcane has no juice,” Mehmood said, showing its stunted growth and dry yellow leaves.
Mehmood is one of millions of Indian sugarcane farmers who is suffering the onslaught of climate change. More intense and longer droughts and floods, caused by climate change, are destroying sugarcane crops and plunging millions of farmers and their families into debt, while creating dangerous working conditions. In August and September, Climate Home travelled to Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh, to hear their stories.
India’s most valuable crop
India is the largest consumer and producer of sugar in the world. Sugarcane is a critical crop for the economy; it accounts for about 10% of the country’s agricultural output and the livelihoods of 50 million farmers and their dependents.
“It is no secret how important sugarcane is to India,” said Devinder Sharma, an independent food and agriculture expert. Further expansion of the sugar industry “needs to be discouraged,” said Sharma. “It is taking too much water.” The crop needs about 2,000 litres of water to produce 1kg of sugar.
“There is just no reason for us to continue pushing for sugarcane when we have options like corn syrup available,” said Sharma. “Rather than looking at adaptation measures, we need to prepare a package to take farmers away from the sugarcane cultivation.”

A tractor ploughs a sugarcane field in Hardoi district, Uttar Pradesh.
Climate impacts
The industry is feeling the impacts of climate change, Mahesh Palawat, vice president of Skymet Weather, a private weather forecaster in India, told Climate Home.
In 2022, India suffered an extreme heatwave and recorded the hottest March in the last 122 years. Maharashtra recorded temperatures of over 46C and in Banda district in Uttar Pradesh temperatures reached 49C. According to a Lancet report, heat-related deaths of people over 65 years increased by 55% in India from 2000-2004 to 2017-2021.
Following the heatwave, Maharashtra experienced heavy downpours [in July and October], which damaged many sugarcane crops, Palawat said. In Uttar Pradesh, there were drought-like conditions until mid-September and “then we suddenly had heavy rain.”
Maharashtra experienced a sixfold increase in floods between 1970 and 2019, according to a report by the Council on Energy, Environment and Water, a Delhi-based think tank.
“Agriculture requires stable weather… these episodes of extreme weather events are harmful,” said Palawat. “What this can result in is that we may have a bumper crop in one region in a particular year but that can quickly change in the next year due to unpredictable weather.”
Intense heat or extreme cold deteriorates the quality of the sugarcane juice and the overall quality of the final sugar product, according to a government report. Temperatures exceeding 35C-40C stunt the growth of the sugarcane crop and reduce the overall yield, according to a 2016 study.
Despite these climate challenges, sugarcane is still considered a better bet than other crops. According to a government report, the net return on cultivating sugarcane is 200–250% higher than for cotton or wheat.
Not enough water
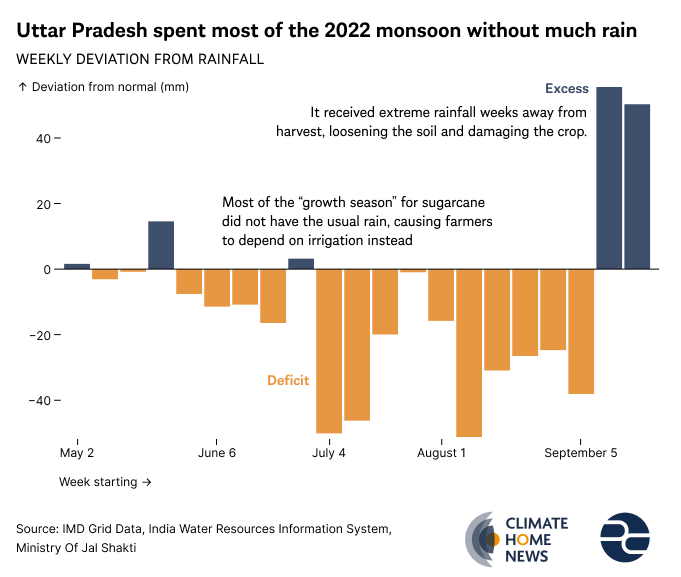
Between May and September 2022, very little rain fell on Uttar Pradesh.
When Climate Home visited Shahabpur in Uttar Pradesh in September, it had just rained for the first time in 40 days. Farm owner Firasut Ali said the area only saw three proper rain spells during the entire monsoon season.
250km away in Uttar Pradesh’s Hardoi district, Ammar Zaidi, a former banker, said that when he started farming in 2014, he was able to secure 40,000-42,500kg of crop per acre. But in the last two years, this has shrunk to about 30,000-36,000kg per acre due to heatwaves. “We are in the thick of the monsoon season but if you touch the ground all you can feel is dust.”
Sitting in his sugarcane field, Zaidi showed Climate Home his diseased sugarcane crop. According to Bharat Rachkar, from the Central Sugarcane Research Station in Maharashtra, when temperatures exceed 40C, “we see the problem of bugs and parasites in the stem”. When temperatures drop below 25C, germination is also affected.
“I have calculated all my inputs and my overall costs. At the end of the day, I am not getting the return [on investment] I need to survive in this profession,” said Zaidi. “If I started making a balance sheet, I would be in the negative every year.”
“For every investment of 100,000 rupees ($1,230), a farmer is only able to secure 90,000 rupees ($1,100),” he said.
“Why am I still doing this? It is probably because like many others in my area my family has been connected to this land and farming for ages. I can’t just leave.”

Labourers prepare sugarcane fields in Sangli district, Maharashtra
Broken dreams
Diljinder Singh, who lives in the village Sheetlapur in Uttar Pradesh, told Climate Home News that he has many broken dreams. He used to work for Jet Airways and live in Gurugram, the swanky neighbouring city of Delhi.
In 2012, he left his job and returned to his village, where his family owns land, to run a sugarcane farm. His parents warned against it. Singh believed that with better sowing and irrigation methods, he could farm in a more productive way. But his harvests languished.
“The whole pattern is disturbed,” Singh said. “About 5-7 years ago, we used to get good rainfall and we didn’t require irrigation but today people are dependent on diesel-run generators to irrigate their fields.”
Too much water
Heat isn’t the only problem. In late September, heavy downpours hit Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra, damaging 2.3 million hectares (23,000 sq km) of crops, including sugarcane. When heavy rains like this hits, it leads to waterlogged soil which impacts the germination process and stunts the root development, said Rachkar.
“I was born in 1989 and until 2006 I had never seen floods in my region. Since then I have seen [floods] three times,” said Ankush Churmule, a farmer whose family has been involved in sugarcane farming for 50 years.
“Areas of western Maharashtra, where the sugarcane is grown near the river, are facing a lot of impact due to successive floods. In those areas, the farmers are moving to bamboo,” said Rahul Ramesh Patil, president of the Weather Literacy Forum, a group that raises awareness about changing weather patterns.

A farmer removes weeds from floodwater in Kolhapur district, Maharashtra, India
The poor harvests caused by excess flooding also impact people with associated livelihoods such as rearing bulls or transporting goods. Kiran Shamrao, who rears bulls for sugarcane farming in Maharashtra, told Climate Home that flooding had severely reduced his profits.
“Our life runs on the bulls. Before, there was little rain, so we had some work for the bulls. But now, because of so much rain, the bulls don’t have work anymore, and we are at a loss,” he said.
Price guaranteed, timing not
If these regions are so prone to droughts and floods, then why do farmers continue to grow sugarcane? The simple answer is that sugarcane fetches them an assured price as it is regulated by the government, unlike other crops such as cotton and soy beans.
“From production to export, every part of the sugar industry is regulated in India. Farmers have an assured buyer and price and they know every last cane will be purchased,” said Sonjoy Mohanty, director of the Indian Sugar Mills Association.
That does not mean payment is swift. Sharma told Climate Home that payments are “often delayed for a year and sometimes even more, bringing hardship to farmers”.
Because of delayed payments, farmers are struggling to make ends meet and are falling into debt, Zaidi said. “Except for sowing, farmers have nothing in their control– neither production nor the final price.”
Representatives for sugarcane farmers told Niti Aayog, the government think tank, that climate threats, such as droughts and floods, “restrict their ability to switch to alternate crops”.
“These weather conditions lead to poor forecasting and the risk of crop failure is higher with other crops [such as cotton, wheat and soybean],” they said.
The Indian government has established a National Agriculture Disaster Management Plan to understand the impact of climate change on farming and focus on disaster risk reduction and possible adaptation measures for the sector.
But farmers told Climate Home they need more support.
No going back
In such a catch-22 situation, what is the solution?
“With climate change being a reality, the crop patterns need to be adjusted otherwise it will heavily impact the yield,” said 50-year-old Suresh Kabade, who has worked as a sugarcane farmer for the past 30 years. “We need to change with climate change.”
A 2019 study by a group of Indian scientists recommended the development of efficient irrigation practices, the adoption of a heat-tolerant cane variety and reducing the use of fossil fuel fertilisers in the near future to assist the sugar industry and help it adapt to the changing climate in northern India.
Other measures could include farmers adopting solar-powered pumps, getting crop insurance, and being taught to use weather forecasting tools, which are readily available but not widely used due to a lack of training.
Most of the farmers Climate Home spoke to were pessimistic about what lies ahead. Singh said there are times when he regrets leaving his corporate job but now there is no option but to continue. “We can’t go back.”
Asked if he will encourage his daughter to follow in his footsteps, Singh was direct. “My nine-year-old daughter enjoys farming and helps me in the fields. Considering my achievements, I would encourage her to take up farming… but if I consider present-day policies, I would never ask her to go into agriculture.”
Reporting by Mayank Aggarwal and Arvind Shukla. Photography by Meenal Upreti. Data visualisation by Gurman Bhatia. The Pulitzer Center supported this project with a reporting grant as part of its Your Work/Environment initiative.