The world may finally be waking to the reality of the climate and ecological crisis, after 30 years of inaction.
But while the UK government has declared a climate and ecological emergency, ongoing plans for airport expansions suggest we’re flying full-speed towards crisis rather than away from it.
Globally, greenhouse gas emissions from aviation are rising rapidly, and set to further escalate. Passenger numbers are rising far too fast for efficiency improvements and alternative technologies, such as electric or biofuel-powered engines, to keep up. What’s worse, the climate impact of flights is two to three times larger than their CO₂ emissions alone, due to the release of nitrogen oxides – powerful greenhouse gases – and the contrails planes leave in their wake which trap even more heat in the atmosphere. The aviation industry has also evaded fuel taxes, emissions regulations, and is often completely omitted in emissions accounting.
This is particularly important as cities are setting targets to reduce their carbon emissions. While many of these cities have airports, their climate strategies tend to focus on the emissions released within the city’s boundaries and from their electricity use. They don’t account for emissions from imported goods and services that are consumed in the city but produced elsewhere, nor from flights through their airports. Any emissions from residents travelling outside the city are generally omitted.
One example is Leeds in the UK, where the city council recently declared a climate emergency and committed the city to emitting no more than 42 megatonnes of CO₂ from 2018 until 2050. But the city’s targets sit uncomfortably alongside plans to expand Leeds Bradford Airport.
The expansion should double the number of passengers using the airport every year from 4m to 8m by 2030. The climate impact of all those flights would be more than double the 2030 target emissions for Leeds as a whole. If passenger numbers continue growing after 2030, even at a slower rate, the overshoot would escalate to a factor of nine by 2040.
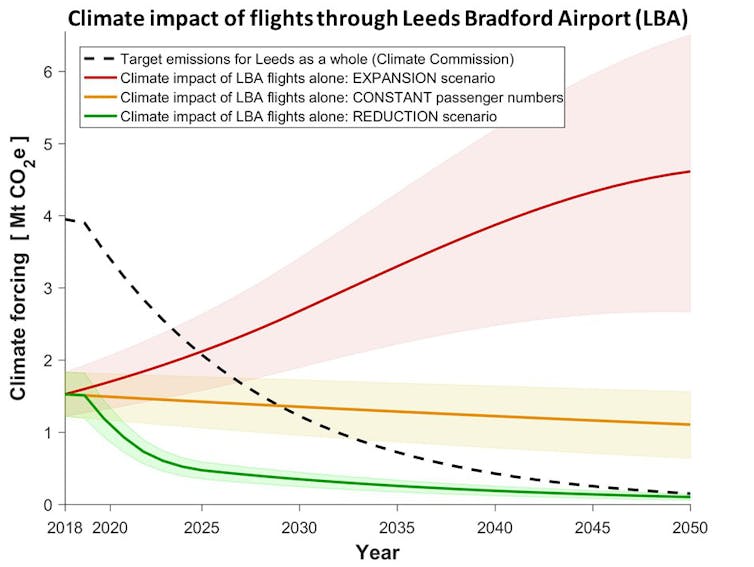
Climate impact of all flights through Leeds Bradford Airport if passengers increase to 8m (red), remain at 2018 level of 4m (yellow) or fall to 1m by 2030 (green), compared to the target emissions for Leeds as a whole (black dashed curve). (Graphic: Jefim Vogel, author-provided)
By 2050, the combined climate impact of all flights through Leeds Bradford Airport since 2018 would exceed the carbon budget for Leeds as a whole by a factor of 2.5. Even if only one in four passengers are Leeds residents, their flights alone would use up 62% of the city’s entire carbon budget by 2050.
As aviation is governed mostly at a national level, Leeds City Council may argue it has little control over the expansion, but is it even trying to stop it? Their Inclusive Growth Strategy suggests the opposite: endorsing the expansion and promising new transport links to the airport with a new commercial centre nearby.
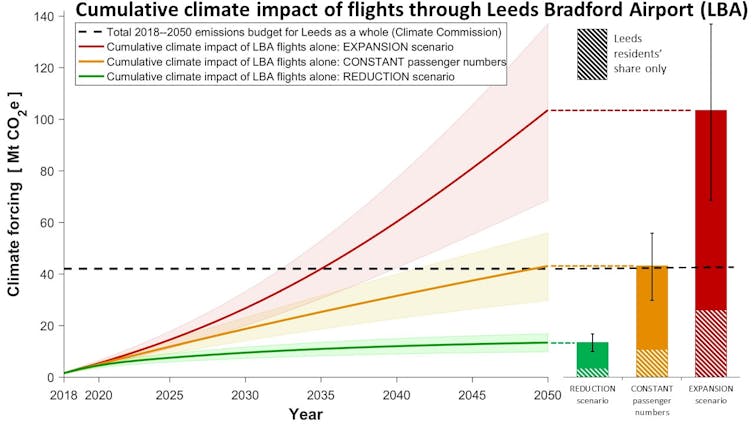
Even if passenger numbers remain at 2018 levels, air traffic at Leeds Bradford would overshoot the city’s carbon budget. (Graphic: Jefim Vogel, author-provided)
If the number of passengers using Leeds Bradford Airport remained at their current levels, all flights from 2018 to 2050 combined would still produce a climate impact equivalent to the entire carbon budget of Leeds. Only if passenger numbers fell drastically could flying become remotely compatible with climate targets.
If cut in half by 2022 and 75% by 2030, the flights of Leeds residents alone would use up 8% of the city’s carbon budget. This might be just low enough to squeeze all other activities in Leeds into the remaining carbon budget – if these are also radically decarbonised.
We need your help… Climate Home News is an independent news outlet dedicated to the most important global stories. If you can spare even a few dollars each month, it would make a huge difference to us. Our Patreon account is a safe and easy way to support our work.
Such a drastic reduction might seem difficult, but perhaps some flights are more dispensable than others. For UK residents, 70% of all flights in 2014 were claimed by just 15% of the population, and while many business leaders fly every week, more than half of the population didn’t fly at all in 2014.
Given how sharply the number of flights has to decrease, the difficult question then is who gets to fly, and for what purpose. Should priority be given to someone taking their fourth flight this year to their second home in the Mediterranean, or to someone visiting their family living abroad? And how is this decided? A first step might be to increase taxes in line with the number of flights a person takes, with what’s called a frequent flyer levy.
But that’s not enough. Price mechanisms can’t make the value judgements at the heart of this – and they could just make flying exclusive to a rich elite who could still afford it. It seems more appropriate to make these decisions through democratic deliberation processes like citizens’ assemblies.
Reducing flights will need to come with wider changes in transport systems and society. A large share of current air traffic could be made redundant by using video conferences for meetings. Improving rail transport could make for a low-carbon and affordable alternative to flying for medium-distance travel. More overnight trains with sleeping facilities and better cross-border integration of rail operators would help. Carefully developing attractive holiday locations closer to home, made accessible by electrified public transport, and promoting low-carbon activities like bike trips could also reduce demand for flights.
Another major issue is car transport which accounts for the lion’s share of transport emissions and causes severe air pollution, with dramatic impacts on public health. Road accidents are a major cause of death worldwide, far exceeding deaths from malaria or war, and road networks and car parks take up lots of public space.
Making transport systems sustainable means ending the dependence on car travel. This involves massively expanding reliable and affordable, low-carbon public transport within and between cities. It also means better urban planning, with more bike lanes, bike sharing and car-free zones. Suburbs should be designed so that a car isn’t necessary for getting around. And a drastically reduced car fleet could be bound to fuel efficiency standards before eventually becoming fully electric.
Deep and rapid changes to the world’s transport systems are needed to halt climate change, and many of these would also improve human well-being and public life. But to get there involves challenging powerful vested interests in aviation and the car and oil industries. The challenges are vast, but doing nothing means accepting an unacceptable future.
Jefim Vogel is a PhD researcher in ecological economics, Joel Millward-Hopkins is a postdoctoral researcher in sustainability and Yannick Oswald is a PhD Researcher in ecological economics, all at the University of Leeds. They receive funding from the Leverhulme Trust through the ‘Living Well Within Limits’ project.
This piece was originally published by The Conversation.
